| Product Code | X0034DVVS2_86754675 |
| GIA Report Number | 5486754675 |
| Shape and Cutting Style | Round |
| Carat Weight | 0.34i |
| Color Grade | Di |
| Clarity Grade | VVS2i |
| Cut Grade | EXi |
| Polish | EXi |
| Symmetry | EXi |
| Fluorescence | NONEi |
| Ultimate Grade | i |
| Measurements | - |
| Table % | 58i |
| Depth % | 61.1i |
| Girdle | -i |
+ Show More | |
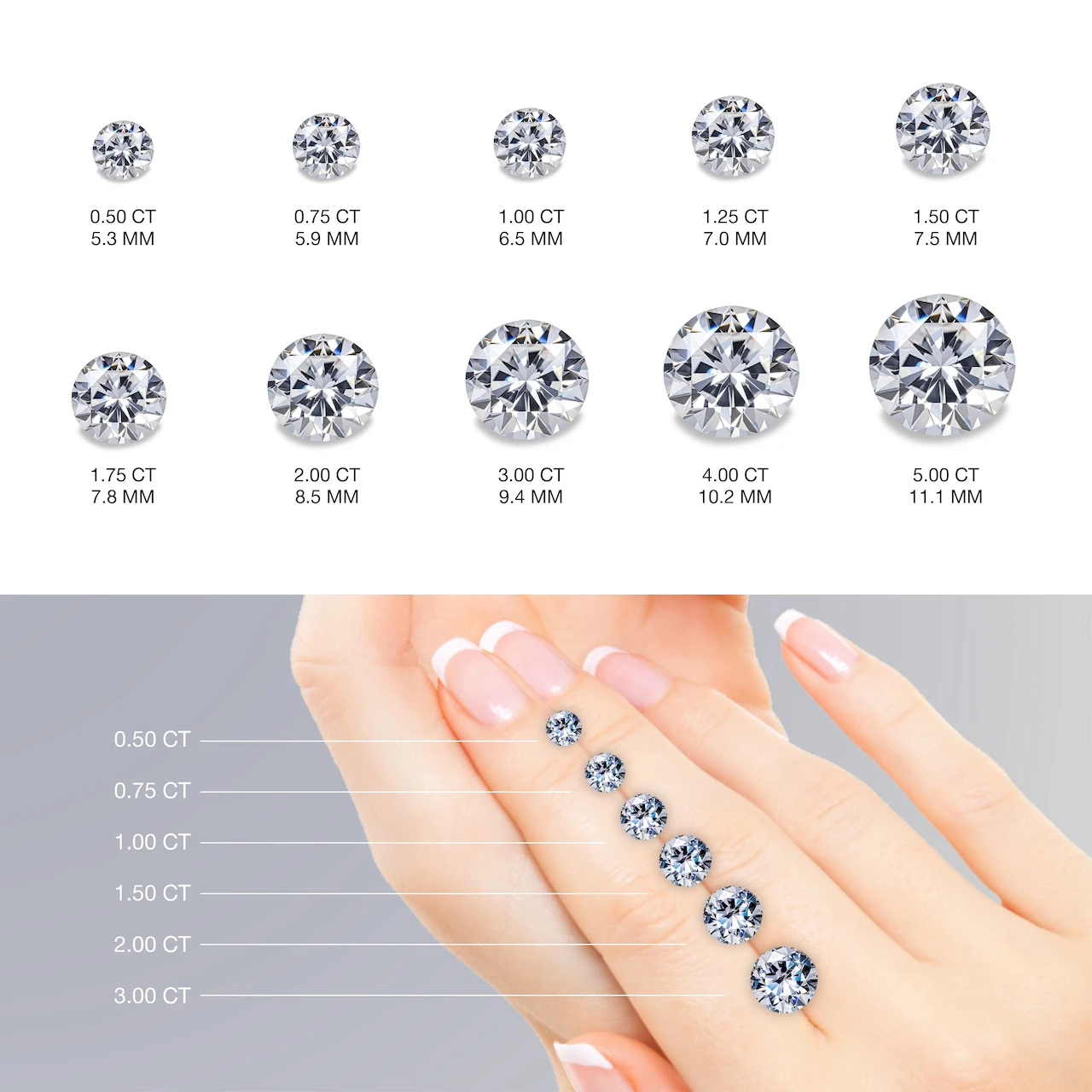
Carat (ct.)
The international unit of weight, used for measuring diamonds and gemstones. 1 carat is equal to 200 milligrams, or 0.2 grams.
The international unit of weight, used for measuring diamonds and gemstones. 1 carat is equal to 200 milligrams, or 0.2 grams.
Diamond clarity refers to the purity of a diamond, indicating the number and severity of its internal and external flaws. These flaws can include inclusions like cotton-like spots or black dots, or blemishes such as cracks. Clarity grades range from FL (Flawless) to I (Included), with FL being the highest and indicating the purest diamond. Factors affecting clarity include the quantity, size, type, location, and visibility of these flaws. Generally, flaws that are not easily visible to the naked eye have a less significant impact on a diamond's value.
The final price of a diamond will be calculated based on
the different tax systems of each country/region.
the different tax systems of each country/region.
Diamond color is graded on a scale from D to Z, with a total of 23 grades. D represents the most colorless and extremely rare grade, while Z indicates a faint yellow hue. Generally, grades D, E, and F are considered colorless.
Fluorescence is the visible blue light observed when diamonds are exposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays.
GIA grading report states if fluorescence is present or not . It also states the strength, or intensity, of the diamond’s reaction to long-wave UV, which is an essential component of daylight. The light emitted lasts as long as the diamond is exposed to the ultraviolet source.
Some diamonds with extremely strong fluorescence may appear hazy or oily which may affect the beauty of the diamond.
GIA grading report states if fluorescence is present or not . It also states the strength, or intensity, of the diamond’s reaction to long-wave UV, which is an essential component of daylight. The light emitted lasts as long as the diamond is exposed to the ultraviolet source.
Some diamonds with extremely strong fluorescence may appear hazy or oily which may affect the beauty of the diamond.
Diamond cutting is the process of shaping a rough diamond into a sparkling gemstone. This process is crucial as it directly influences the diamond's brilliance and fire. A well-cut diamond has optimal proportions, symmetry, and polish, allowing light to reflect multiple times within the stone, creating a dazzling display. It's like creating a perfect stage for the diamond to showcase its beauty. Cut grades typically range from Excellent to Good, with higher grades indicating more brilliance. A well-cut diamond is more dazzling and valuable.
Diamond polishing is the final and crucial step in the diamond cutting process. It involves using specialized tools and techniques to smooth and polish the diamond's facets to a mirror-like finish. The purpose of polishing is to maximize the diamond's ability to reflect light, creating a brilliant display of fire. The quality of the polish directly affects the diamond's luster and overall appearance. The polishing process typically involves diamond powder and high-speed polishing wheels. Skilled artisans are required to achieve a flawless polish on each facet of the diamond. The polish grade is a significant factor in diamond evaluation, with higher grades indicating a finer polish and greater brilliance.
The precision and alignment of a diamond's facets and the resulting effects on its brilliance.
The diamond's fire grade is a crucial indicator for evaluating the quality of its cut. It measures the degree to which light is reflected and refracted within the diamond after cutting, resulting in a rainbow-like sparkling effect. A higher fire grade indicates a stronger sparkle and a more dazzling diamond. Fire grades are typically categorized into excellent, very good, good, and fair.
Length-to-width ratio
Length (L) divided by Width (W) is the Length-to-Width ratio. This conveys how relatively square or rectangular a fancy-shaped diamond appears when viewed from the top.
Length (L) divided by Width (W) is the Length-to-Width ratio. This conveys how relatively square or rectangular a fancy-shaped diamond appears when viewed from the top.
Table percentage
The width of the diamond's table expressed as a percentage of its average diameter. A component of the overall cut grade, this measurement is critical to a diamond's light performance.
The width of the diamond's table expressed as a percentage of its average diameter. A component of the overall cut grade, this measurement is critical to a diamond's light performance.
Depth percentage
The height of a diamond, measured from the culet to the table, divided by its average girdle diameter. One of the basic proportions that contributes to a diamond's appearance, brilliance and fire.
The height of a diamond, measured from the culet to the table, divided by its average girdle diameter. One of the basic proportions that contributes to a diamond's appearance, brilliance and fire.
Where the crown and pavilion meet, defining the diamond's outline. Avoid extremely thin girdles, which can make a diamond more prone to damage, or extremely thick, which can cause the diamond to look smaller than diamonds of similar weight.
Culet
The facet or point at the bottom of a diamond pavilion. In preferred diamond cut grades, culets are generally undetectable to the unaided eye and graded none to small. Medium to large culets may have an impact on light performance.
The facet or point at the bottom of a diamond pavilion. In preferred diamond cut grades, culets are generally undetectable to the unaided eye and graded none to small. Medium to large culets may have an impact on light performance.
0.34 Carat D-VVS2 Excellent 圓形 Diamond
0.34ct
D Color
VVS2 Clarity
EX Cut
USD 0
(Price) i
USD 0
(+GST)
Market Price
USD 0
Choose top-grade diamonds certified to international standards, meeting your 4Cs requirements. We ensure transparent pricing, keeping you informed about market trends.
Diamond certification
+
Diamonds above 0.3 carats come with GIA or IGI certification, clearly detailing their characteristics.
Lifetime after-sales services
+
Lifetime after-sales services, ensuring your ring lasts.
Excellent price-quality ratio
+
We bring you diamonds with an excellent price-quality ratio. Let our specialists advise you.
Excellence in Quality and Unmatched Value Commitment
Experience unparalleled quality assurance with our meticulously selected internationally certified diamonds. Each stone meets the highest standards in carat, color, clarity, and cut, accompanied by detailed certification. We uphold transparent pricing and offer global cleaning, polishing, and maintenance services for all products, ensuring an exceptional experience and enduring quality.
After-Sales Care Service
+
Enjoy lifetime free cleaning. Your first resizing, polishing, and repair service is on us.
Engagement Ring Borrowing Service
+
Borrow an engagement ring for your proposal. Once your proposal is successful, return to the store to select the perfect ring.
Gold Set Rental Service
+
With any ring purchase, take advantage of our complimentary gold jewelry set rental service.
Ring Fingerprint Engraving Service
+
Personalize your rings with our fingerprint engraving service, capturing both of your fingerprints inside the band.